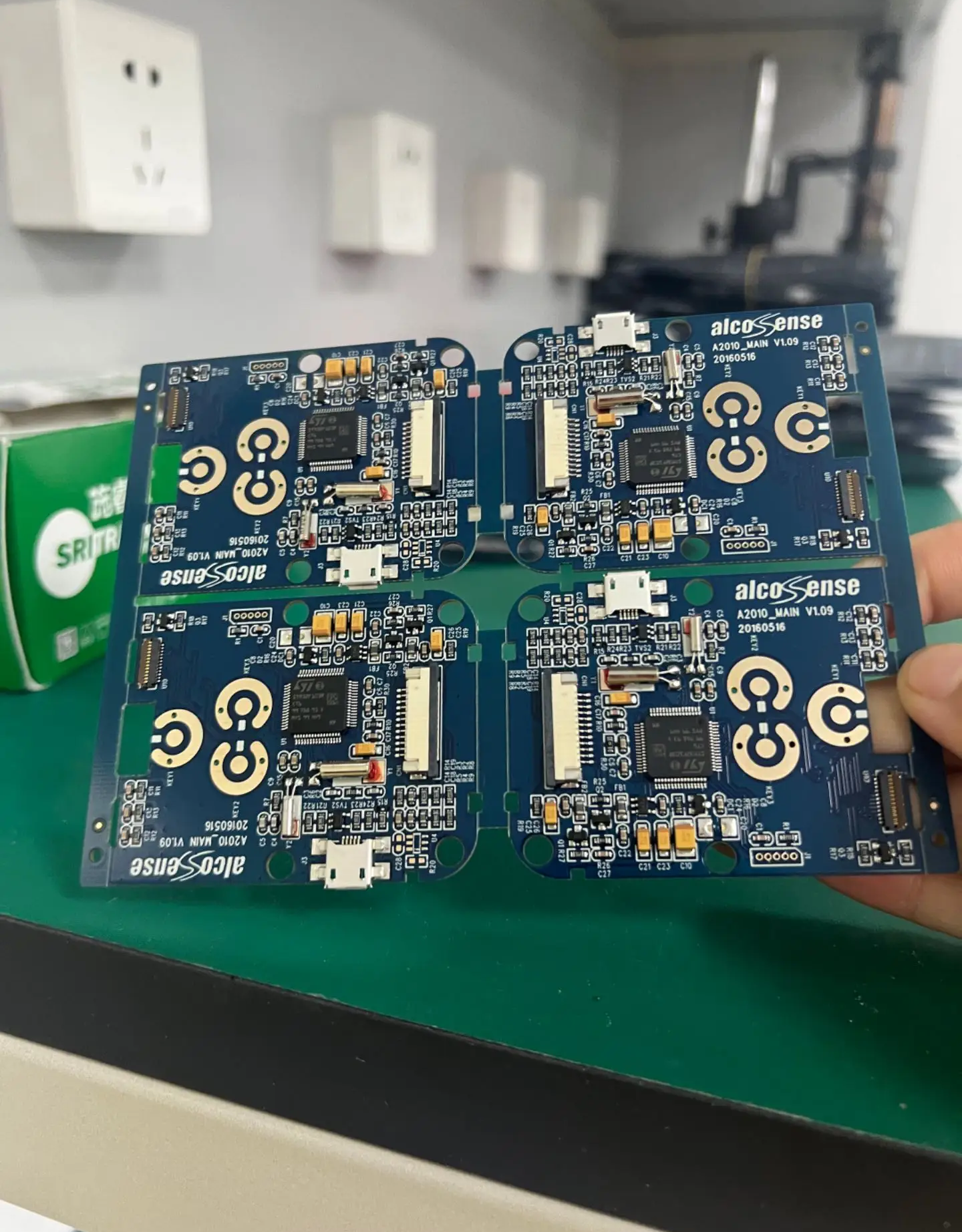
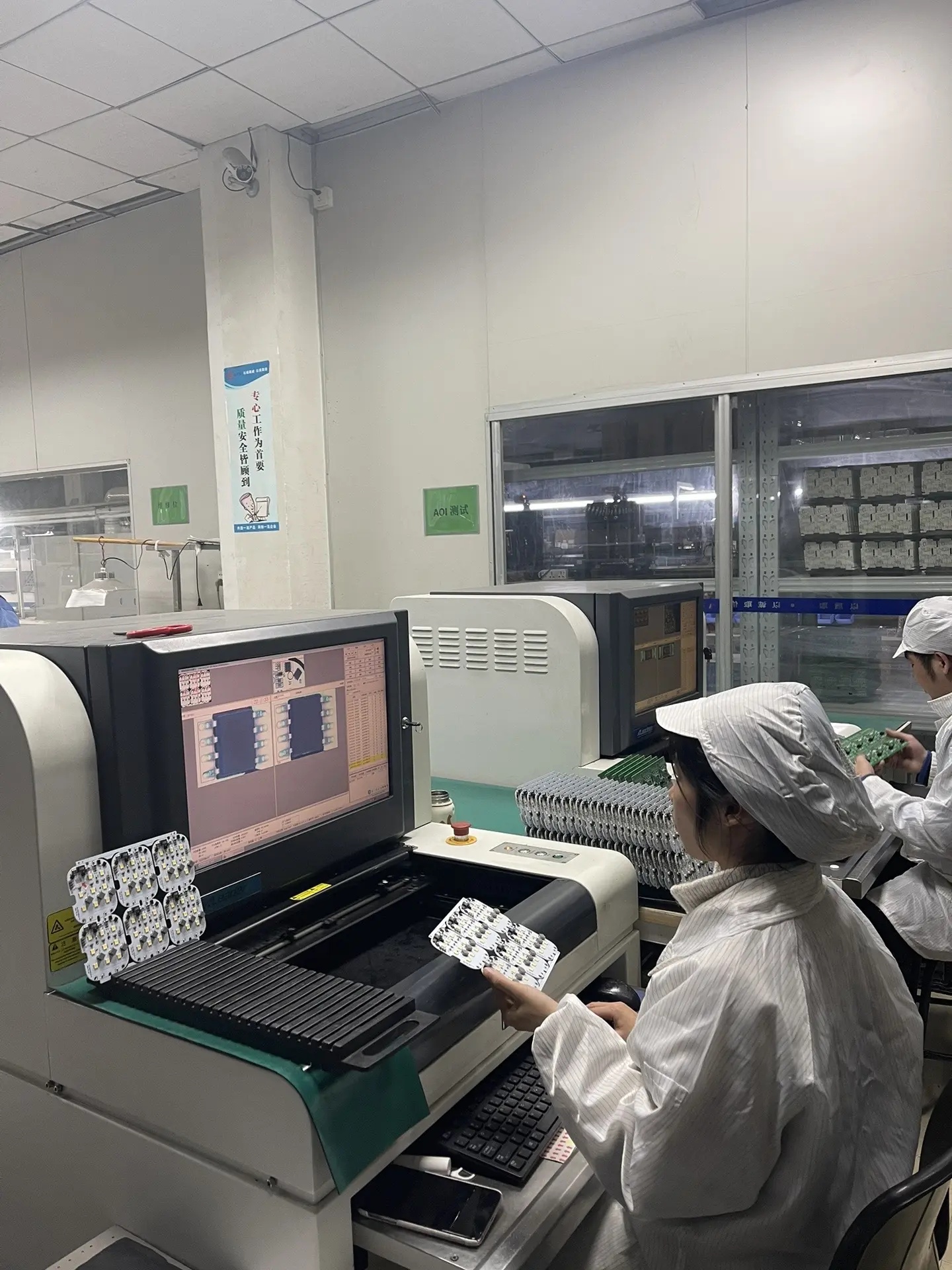
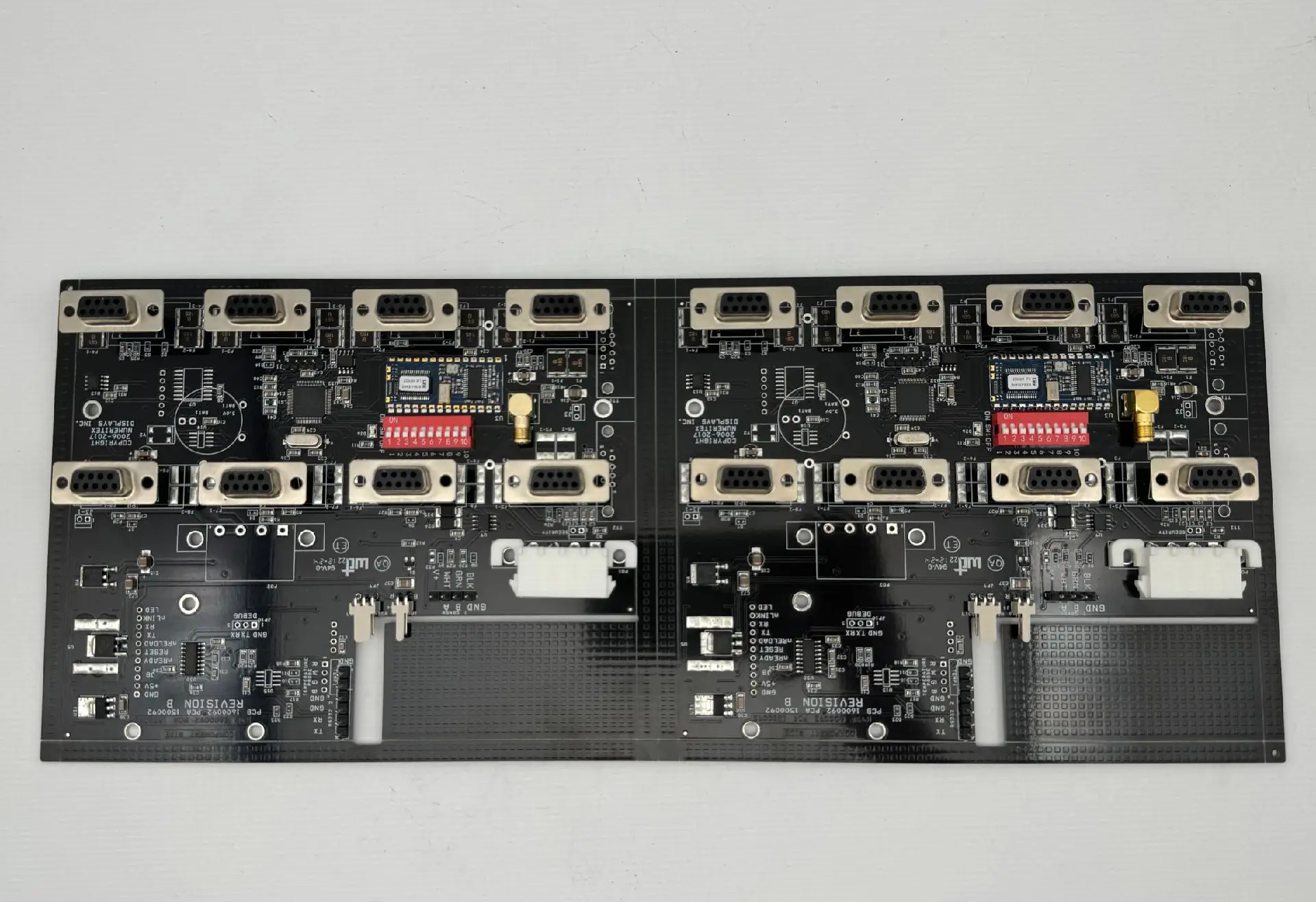
PCB drilling is a critical process in printed circuit board manufacturing. Below is a detailed explanation:
Functions
- Electrical connection: By drilling through-holes, blind holes, or buried holes in the PCB, electrical conduction between different layers is achieved through metallization of the holes. This allows electronic components to be interconnected as designed, forming a complete circuit.
- Component fixation: Provides mounting positions for component leads, enabling precise soldering onto the PCB and ensuring stability and reliability of electronic devices.
Drilling Equipment
- CNC drilling machines are typically used for PCB drilling. These devices offer high precision and efficiency, accurately controlling drill position and depth based on pre-designed drilling files.
Process Flow
- Board loading: Fix the cut PCB substrate on the drilling machine’s worktable, ensuring it is flat and correctly positioned for subsequent drilling.
- Drilling: The CNC drilling machine drives the drill bit to bore holes in the PCB at a specified speed and feed rate according to design files. During drilling, parameters such as drill speed must be adjusted based on substrate material, thickness, and hole diameter to ensure quality.
- Board unloading: After drilling, remove the PCB from the worktable for subsequent inspection and processing.
Quality Control
- Hole diameter accuracy: The drilled holes must match design specifications, with errors controlled within a defined range. Deviations may cause component leads to fail to insert properly or result in poor electrical performance after hole metallization.
- Hole position accuracy: Hole locations must be precise, with minimal deviation from design coordinates, to ensure correct component placement and avoid short circuits or open circuits.
- Hole wall quality: The hole walls should be smooth, free of burrs, cracks, or delamination. Good hole wall quality enhances the adhesion and electrical performance of hole metallization.
10203 View